Design Criteria
The deflection limits that are used for member design.
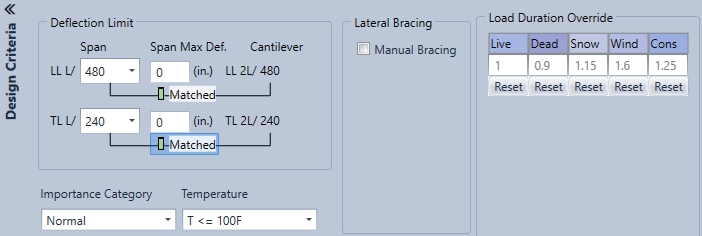
Deflection Settings
Deflection Limit
How much a structural element bends under a load.
Span (Deflection Settings as a Ratio)
This is the deflection limit and is a predefined number. If users would like to enter a custom number they are also able to do so.
L/value, where: L= member length (in) value= min. 360 for floor beams/joists live load deflection; 240 for floor beams/joists total load deflection; 240 for roof beams/rafters live load deflection; 360 for roof beams with gypsum ceiling for live load deflection; 180 for roof beams/rafters total load deflection
Span Max. (Deflection Setting as an Absolute Dimension)
Allows users to enter deflection in inches (example: maximum deflection= 0.5")
Cantilever
It will perform the deflection check on the cantilever portion (in above picture that is the 180 area).
If a user checks 2L/ it will double the cantilever to 360 instead of the 180. Which then makes the cantilever more stiff.
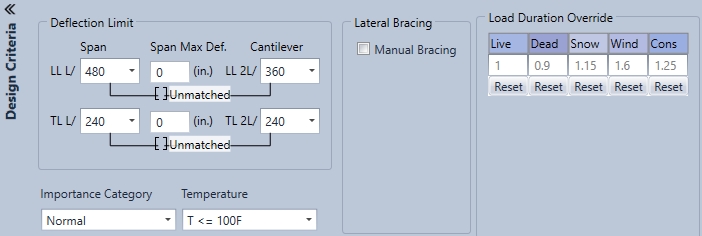
LL (Live Load)
Reflects a moving variable or weight added to dead load
TL (Total Load)
The complete measurement of live and dead load together
Load Duration Override
The user can override the load durations factors that are automatically implemented in the application
Lateral Bracing
Bracing to prevent the lateral displacement of the member
All bending members are deigned in accordance with the lateral stability calculations (as per NDS/CSA-USA/Canada design standards)
Automatic vs. Manual Bracing
The user can enter a specific distance/length/o.c. spacing where the lateral braced will be installed
Manual Bracing Settings
Allows the user to manually select bracing for a member
Importance Category
For the purpose of determining the specified snow and wind loads. Importance factors will be applied in accordance with ICC/IRC or NBCC building codes from USA and Canada, respectively
Temperature
When structural members will experience sustained exposure to elevated temperatures, design values will be multiplied by the temperature factors